Nearly 37 million people are living with HIV around the world. In the United States, 1.2 million people are living with HIV, of whom 13 percent are unaware of their diagnosis. Although progress has been made in the global fight against HIV/AIDS, the epidemic continues in the United States and the international community
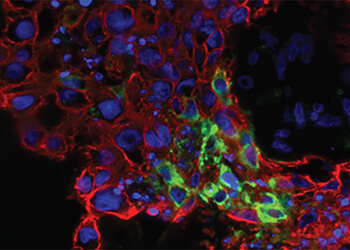
HPMI scientists are conducting a wide range of basic research activities aimed at better understanding the pathology of Zika &; Dengue. New research findings are shedding light on the mechanisms of infection, such as how the virus enters the cells and how the human immune system responds to the infection.
HPMI scientists are conducting a wide range of basic research activities aimed at better understanding the pathology of Zika &; Dengue. New research findings are shedding light on the mechanisms of infection, such as how the virus enters the cells and how the human immune system responds to the infection.
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections transmitted from an infected person to an uninfected person through sexual contact. STDs can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Examples include gonorrhea, genital herpes, human papillomavirus infection, HIV/AIDS, chlamydia, and syphilis.
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious and often severe airborne disease caused by infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) bacteria. TB typically affects the lungs, but it also can affect any other organ of the body. It is usually treated with a regimen of drugs taken for six months to two years depending on whether the infecting organisms are drug resistant.
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious and often severe airborne disease caused by infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) bacteria. TB typically affects the lungs, but it also can affect any other organ of the body. It is usually treated with a regimen of drugs taken for six months to two years depending on whether the infecting organisms are drug resistant.